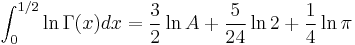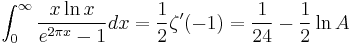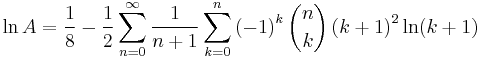Glaisher–Kinkelin constant
In mathematics, the Glaisher–Kinkelin constant or Glaisher's constant, typically denoted A, is a mathematical constant, related to the K-function and the Barnes G-function. The constant appears in a number of sums and integrals, especially those involving Gamma functions and zeta functions. It is named after mathematicians James Whitbread Lee Glaisher and Hermann Kinkelin.
Its approximate value is:
The Glaisher-Kinkelin constant  can be given by the limit:
can be given by the limit:
where 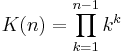 is the K-function. An equivalent form involving the Barnes G-function, given by
is the K-function. An equivalent form involving the Barnes G-function, given by ![G(n)=\prod_{k=1}^{n-2}k!=\frac{\left[\Gamma(n)\right]^{n-1}}{K(n)}](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/f53602e8f206563c54b5dee9b4eb9bf2.png) where
where 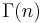 is the gamma function is:
is the gamma function is:
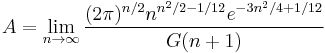 .
.
The Glaisher-Kinkelin constant also appears in the Riemann zeta function, such as:
where 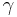 is the Euler–Mascheroni constant.
is the Euler–Mascheroni constant.
Some integrals involve this constant:
A series representation for this constant follows from a series for the Riemann zeta function given by Helmut Hasse.
References
- Jesus Guillera and Jonathan Sondow, Double integrals and infinite products for some classical constants via analytic continuations of Lerch's transcendent,Ramanujan Journal 16 (2008), 247–270. (Provides a variety of relationships.)
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Glaisher–Kinkelin Constant" from MathWorld.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Riemann Zeta Function" from MathWorld.
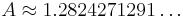
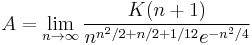
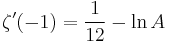
![\sum_{k=2}^\infty \frac{\ln k}{k^2}=-\zeta^{\prime}(2)=\frac{\pi^2}{6}\left[12\ln A-\gamma-\ln(2\pi)\right]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/3a66a6fd56cfc18299e579af892da263.png)